Upcoming Spring 2025 Courses
Interested in taking philosophy courses this upcoming spring? Below, you'll find the courses we're offering for both the January term and the regular Spring semester. Just as an FYI: click on the posters if you want to see the full image!
J-Session Courses
January 3rd - 20th, 2023
Logical Reasoning for Standardized Graduate Exams
What does it mean to be an engaged critical reasoner? Some think it is simply to be contrarian. This course will challenge that view by emphasizing reasoning activity as systematic and rigorous. This course will include argument construction and assessment, deductive and inductive logics, formal deductive logic, and the identification of fallacies and their avoidance. It will also challenge the students to address real-world issues!
Spring 2025 Courses

PHIL 1010
Introduction to Philosophy
The Meaning of Life
What does it mean to live a good life?
This course will challenge students to think about why they have come to college, what their next steps are, how a liberal arts education can prepare them for what comes down the road, and what is ultimately meaningful in life.
The course will include philosophical, literary, and psychological examinations of happiness, freedom (how do we make transformative life decisions), the value of college education, materialism/consumerism, and resilience in the face of suffering and mortality.
In short, you will work at answering the fundamental question:
What is the meaning of it all?
This class fulfills the
Humanities & Fine Arts General Education
requirement.

PHIL 1020
Contemporary Moral Problems
An introduction to the application of basic moral concepts and theories to contemporary moral issues. Discussion topics will vary and may include: distribution of wealth and resources, capital punishment, torture, environmental ethics and sustainability, animal rights, euthanasia, abortion, cloning, genetic engineering, privacy rights, drug laws, marriage and sexuality, gun control, and affirmative action.
This class fulfills the
Humanities & Fine Arts General Education
requirement.

PHIL 1020
Contemporary Moral Problems
Civil Discourse
In-Person TR 10:00-11:15
This special section of Contemporary Moral Problems will have a focus on developing the skills and perspective to engage in Civil Discourse. While investigating a wide range of ethical and moral problems, we will discuss contentious issues in way that promotes mutual understanding. The essence is respect, trust, and a desire to find common ground. Although it is unlikely that we will reach consensus, we will aim for mutual understanding. This course is not about proving you are right, it is about deepening your appreciation of central arguments and trying to understand the views of those with different values and perspectives. In the end, we aim to improve our ethical understanding and usefully engage those with whom we have seemingly fundamental disagreements.
This class fulfills the
Humanities & Fine Arts General Education
requirement.

PHIL 1030
Introduction to Philosophy
Brains, Minds, and Machines
This course examines central questions in philosophy about the nature of the mind, the self, human rationality, perception/experience, and technology through the lens of work in cognitive science, neuroscience, artificial intelligence, and psychology. Some major topics and questions include: What are minds? Is the human mind a digital computer? Could a machine—e.g., a robot or a computer—be truly intelligent, or have experiences like humans and animals do? How does the brain “represent” its environment? In engaging these questions, the course also introduces students to foundational issues in cognitive science and artificial intelligence including: nativism vs. empiricism, mental representation, classical artificial intelligence vs. neural networks, modularity, evolutionary psychology, embodied cognition, and extended cognition.
This class fulfills the
Humanities & Fine Arts General Education
requirement.

PHIL 1050
Introduction to Philosophy
Philosophy, Technology, and Science Fiction
Evil robots! Mad scientists! Alien intelligences! This course introduces core philosophical ideas through a selection of accessible science fiction short stories and films. Does a society's technology determine its values and development? Does technology reflect our values or is it neutral? How do the development of new technologies help and harm people? What is a technological singularity? We will be exploring these questions in the philosophy of technology through how technological advances have been presented in science fiction. In addition, we will also be exploring the philosophical issues around how biological systems could be manipulated. What are the prospects and dangers of biohacking? What are the boundaries of what makes us human? How could different life and ecosystems evolve? Should there be scientific research that shouldn’t be done? Additional topics may include: Could I be deceived about the external world? Do we act freely or is everything predetermined?
This class fulfills the
Humanities & Fine Arts General Education
requirement.

PHIL 1210
Critical Reasoning
What does it mean to be an engaged critical reasoner?
Some think it is simply to be contrarian. This course will challenge that view by emphasizing reasoning activity as systematic and rigorous.
This course will include argument construction and assessment, deductive and inductive logics, formal deductive logic, and the identification of fallacies and their avoidance. It will also challenge the students to address real-world issues!
This class fulfills the
Humanities & Fine Arts General Education
requirement as well as requirements for
Philosophy (BA – All Concentrations and Minor),
Psychology (Advocacy, Ethics, Social Justice & Law Cognate Requirement, BS),
Neuroscience (Cognate Requirement, BS),
and is recommended for
Medical Humanities (Minor).
PHIL 2010
Symbolic Logic
This course covers the central aspects of propositional logic and predicate logic. We study both semantics (i.e., interpretive relations between language and subject matter including notions such as truth and reference) and syntax (i.e., formal relations between elements of language). We learn how to construct and translate formal languages and explore the basis of both semantic and syntactic inference. We also explore foundational issues in logical metatheory. Throughout the course, we discuss broad philosophical themes such as the purpose of language, constraints on translation, and the nature of meaning itself.

PHIL 2030
Introduction to Ethics
What is good? What is right?
What should you do?
In this class, students learn essential moral distinctions and influential moral theories and learn to apply these in the deliberation of complex ethical issues. At the heart of it all is discussion. Discussion of the theories and their application is central to learning how to reason about ethical problems and make moral progress.
This class fulfills the
Humanities & Fine Arts General Education
requirement as well as requirements for
Nursing Programs (UNMC - Prerequisite),
Medical Humanities (BA, BS, and Minor),
Psychology (Advocacy, Ethics, Social Justice & Law Cognate Requirement, BS),
Neuroscience (Cognate Requirement, BS),
Holocaust and Genocide Studies (Minor),
Human Rights (Minor),
Ethics (Minor), and
Philosophy (BA: All Concentrations and Minor).

MEDH/PHIL 2300
Biomedical Ethics
In the rapidly evolving fields of medicine and healthcare, ethical considerations play an ever-increasing role. This course is designed to equip students with the conceptual tools necessary for ethical reasoning and decision-making in medical contexts. This course investigates critical issues such as informed consent, end-of-life decisions, reproductive ethics, genetic testing, and research ethics. Ideal for students thinking about a career in healthcare, philosophy majors, medical humanities majors, or anyone interested in grappling with the complex ethical questions that accompany advancements in biomedical science and healthcare practice.
This class fulfills requirements for
Nursing Programs (UNMC - Prerequisite),
Medical Humanities (BA, BS, and Minor),
Psychology (Health and Science Explorations Cognate, BS),
Neuroscience (Medical Humanities Path, BS),
Ethics (Minor),
Ethics, Law, and Social Political Philosophy
Concentration of Philosophy (BA), and
Philosophy (Minor).

PHIL 3000
Philosophy Writing
This course focuses on writing instruction, with particular emphasis on editing and revision, the use of logical argument structures, and proper research and citation methods. Significant quantities of both formal and informal writing will be required throughout the semester.
Philosophy Writing is ideally suited to students who are beginning to take upper-level coursework and wish to develop more sophisticated skills in argument-based writing. Although most students who take the course are Philosophy majors or minors, it is open to students from any major, especially those in which logic, mathematics, or other symbolic languages may be used to construct arguments.
In addition to being
REQUIRED for ALL Philosophy Majors
(ALL Concentrations),
this course also fulfills
the Advanced Writing Requirement for
Mathematics (BS).

PHIL 3040
Philosophy of Law
What is the law and how is it created? What makes legal authority legitimate, and what are its limits? What is the relationship between law and morality? What are legal rights and how should they be protected?
This course explores these questions and many others, including competing theories about the nature of the law and legal reasoning, constitutional interpretation, and punishment.
taught by
William O'Brien
Attorney
This course fulfills requirements for
Psychology (Advocacy, Ethics, Social Justice & Law Cognate Requirement, BS),
Ethics, Law, and Social Political Philosophy
Concentration of Philosophy (BA),
Human Rights Studies (Minor),
Ethics (Minor),
and as an elective for
Philosophy (BA: Other Concentrations and Minor).
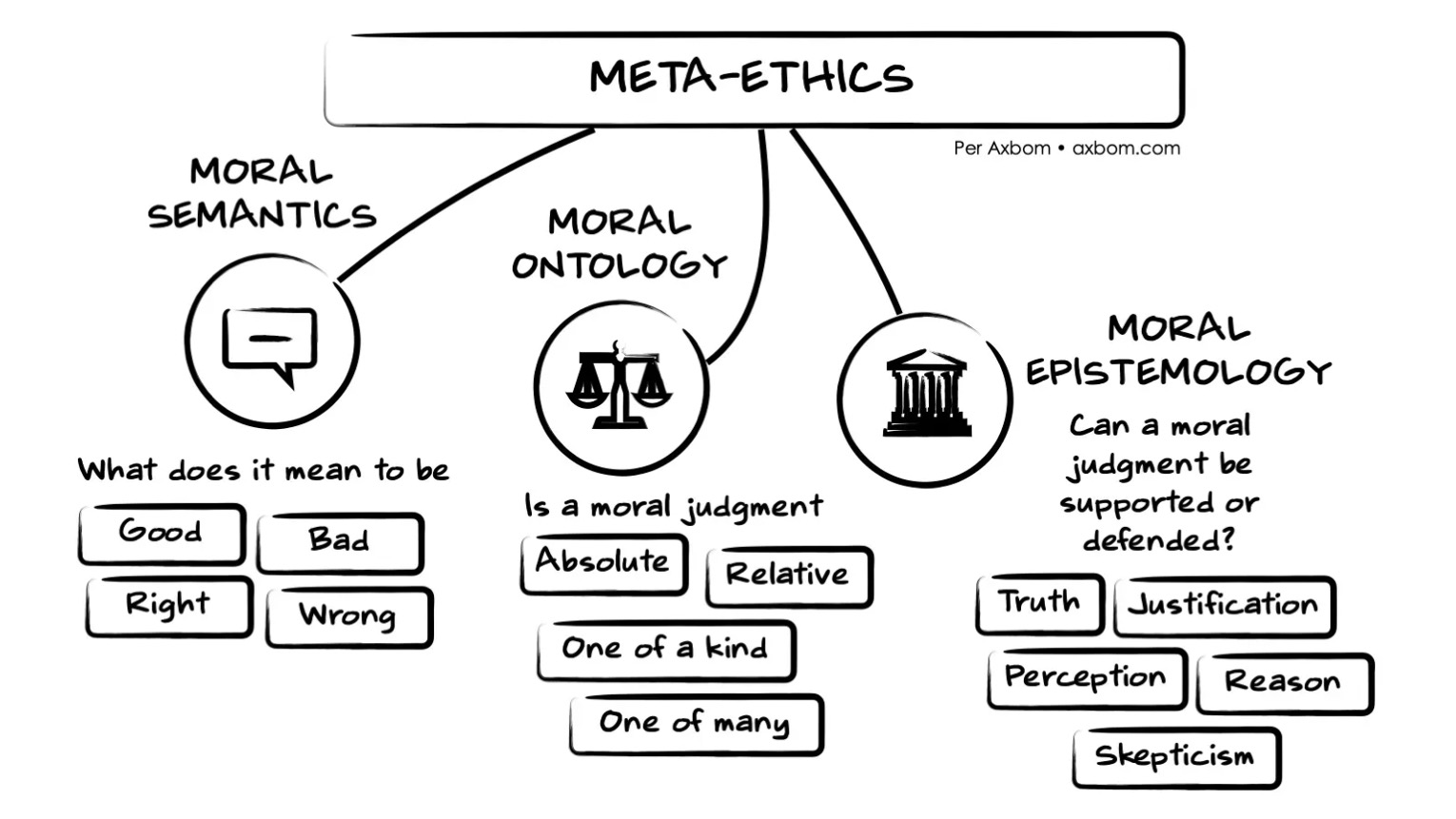
PHIL 3050
Ethical Theory
This course includes a detailed examination of selected topics in normative ethics and/or metaethics. Normative ethical questions to consider may include: Is the morally right thing to do always the thing that has the best consequences, as so-called "consequentialists" believe? What sorts of things are intrinsically good, i.e., good in themselves, regardless of their effects?
Metaethical questions to be considered may include: Are there any objective moral facts? If so, where do they come from?

PHIL 3070
Leadership Ethics in Practice
Reserved for
Bachelor of Multidisciplinary Studies (BMS)
Students only.
In today's complex and interconnected world, ethical leadership is a necessity. Ethical leaders inspire trust, foster a positive organizational culture, and drive sustainable success. This course aims to equip future leaders with the essential moral knowledge and reasoning skills required to navigate the broad and difficult challenges they will confront. In particular, students will study the philosophical foundations of ethical leadership, examine how these illuminate historical and contemporary cases of leadership success and failure, and apply the lessons to their own experience. In short, this course aims to cultivate the ethical leadership skills that will not only propel careers but will help students meaningfully contribute to a better, more responsible world.

PHIL 3110
Ancient Greek Philosophy
What does it mean to lead an examined life? What did Socrates, Plato, Aristotle, Epicurus, the Stoics, and others think about the nature of the universe and how to live the best life?

PHIL 3130
History of Modern Philosophy
What is the nature of our cosmos and how can we know anything about it with certainty? Can we provide successful arguments to demonstrate that God exists, or to explain the nature of the human mind and its relationship to the body? Can we provide adequate justification for any of our causal inferences? What is the foundation of human rights and moral obligations? This course explores the revolutionary ideas of philosophers in the modern period that continue to shape the contours of contemporary philosophical thought.
In Western Philosophy, the Modern period (around 1600 to 1800) was a time of great scientific advancement, political upheaval, and philosophical progress. During this period, philosophers including Bacon, Descartes, Locke, Hume, Spinoza, and Leibniz wrestled with fundamental metaphysical questions about the nature of matter, causation, mind, and God, epistemological problems concerning the nature and grounds of knowledge, and ethical and political questions about our rights and duties. The philosophical work of this period provides the foundations for contemporary work in epistemology, metaphysics, philosophy of mind, philosophy of science, ethics, and political philosophy.

PHIL 3210
Social Philosophy
Topics will include: Robert Paul Wolff on Anarchy and Democracy; Jan-Werner Müller on Real and Fake Democracy; David Livingstone Smith on Inhumanity; Ethno-Nationalist Conflicts and Democracy and Peace Building; Evocative Objects, Neighborhoods, and Democracy; and many others.

PHIL 3220
The Philosophy of Art
An inquiry into historical and contemporary philosophical perspectives on the making, interpreting and criticizing of works of art, including relations of the arts to other dimensions of culture. This course will address questions such as "what is a work of art?," "what is beauty?," "can art be immoral?," "what is the relationship of art to politics, and to peace and democracy building?,” and “what is the point of throwing mashed potatoes on a Monet painting?”

PHIL 3400
Philosophy of Natural Science
This course will offer an examination of the philosophical problems associated with the methods of the natural sciences, the presuppositions of scientific inquiry, and the nature of scientific laws and theories.

PHIL 3410
Philosophy of Social Science
Philosophy of Social Science focuses on how presumably
PHILOSOPHY and SCIENCE
work within any SOCIAL phenomenon.
Through intensive and extensive conversational “lectures” (a series of village roundtable-like “dialectic”), course participants explore how certain “foundational” philosophical frameworks (such as social ontology/social epistemology) and certain science concepts co-examine social goods(be they physical, mental, economic, or axiological). In other words, the course examines how the human being apparently always manages to live simultaneously alone and with others amid questions about “money”… (economics), “wellbeing”… (psychology), “control” … (political science), “origins” … (anthropology), and “groupings” … (sociology). This course should be of interest to students in such disciplines as economics, psychology, sociology, anthropology, history, medical humanities, criminology and criminal justice.

PHIL 3500
Animal Minds and Animal Ethics
• Over the past few decades there has been an explosion of research on animal consciousness. In this class, we will study three separate but interrelated issues: questions of animal consciousness, issues related to the study of animal consciousness, and how current understandings of animal consciousness should impact our treatment of animals. Some topics we will cover include: whether animals have beliefs and desires, whether animals have a conception of the self, problems of measuring animal consciousness, whether death can be bad for animals, and how considerations of autonomy might affect the permissibility of animal captivity.
Crosslisted with PSYC and ENVN.

PHIL 3510
Phenomenology and Existentialism
Phenomenology and Existentialism will focus on Husserl’s phenomenology as a philosophical discipline, especially its twin concept of “transcendental consciousness” and “Lebenswelt”; thereafter, we will examine phenomenology’s implications for or relationships to existential philosophy as primarily a 20th-century global ism (or philosophical phenomenon or movement). Through intensive and extensive conversational “lectures” (a series of village roundtable-like “dialectic”), we will cover certain primary texts by Brentano, Husserl, Heidegger, Sartre, Merleau-Ponty, De Beauvoir, Fanon, Stein, Arendt, and Camus.

PHIL 3650
Philosophy of Mind
A discussion of various accounts of the nature of minds which focuses upon philosophical problems such as whether the mind is identical with the brain, the extent of similarities between human minds and computers, the nature of personal identity, and the relationship of mental activity to behavior.
This course will address questions such as: What is the nature mind? Is mind a unique sort of substance, just a program, or nothing at all? Do minds really have an effect on the world? If so, how? Could physical science ever explain the nature of mind? Could mind be somehow a fundamental constituent of reality?
This course fulfills requirements for
Psychology(BS).
Crosslisted with PSYC.

PHIL 3700
Space, Time, and Reality
The world appears to contain two types of things: objects and their properties. These objects, we believe, exist and interact with one another in time and in space. But there are many questions in need of answers. Must all objects exist in time and space? What is time, and how should we understand our passage through it? What exactly is an object, and how is it related to its parts? What relationship does it bear to its properties? What does it mean for an object to change? What is space, and how does it relate to time? Are the laws of physics necessarily deterministic, and, if so, to what extent can we truly be said to be free?
In this class, we attempt to address these questions and many more. As we will quickly learn, reality is not as it appears.

PHIL 4240
Philosophy of Emotion
In this class, we will aim to understand emotions, moods, attitudes, and other affective phenomena from a broad, empirically informed perspective while keeping both practical and philosophical issues in mind. We will ask questions such as: What are emotions, moods, and the rest? How are these various affective phenomena related to one another? Are some emotions basic and universal? How do language and culture shape our affective experiences? How do emotions and moods provide information about our relationship to the world? Under what conditions are emotions and moods appropriate or inappropriate? What role do they play in our reasoning and decision-making? What role do they play in our ethical lives? What role do they play in the arts (e.g., music, literature, film)?

PHIL 4250
Limits of Consciousness
We all live lives rich in subjective experience. And yet consciousness is often considered one of the most mysterious and unexplained features of our world. Limits of Consciousness examines the philosophy, neuroscience, and psychology of consciousness. Topics we may explore include: what is consciousness? What are different kinds of consciousness? Is there such a thing as unconscious perception? What are the major scientific theories of consciousness, and are they any good? Where is consciousness located in the brain? Are animals conscious? This class is an interdisciplinary inquiry into the nature of consciousness and whether and how science can explain it.

PHIL 4260
Moral Psychology
The growing interdisciplinary field of moral psychology studies our moral beliefs and decision- making processes using the tools of anthropology, psychology, philosophy, and neuroscience. Topics in the science of morality will include the moral-conventional distinction (the distinction between moral norms and non-moral norms such as etiquette), the role of reasons vs. emotions in moral judgment, the brain basis of moral decision-making, cultural differences in moral norms, psychopathy, and the development of morality in children. Psychology studies the nature of moral judgment using behavioral tasks. Neuroscience employs techniques such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), and other tools for monitoring and manipulating brain processes to study “where” in the brain moral decision making occurs and the nature of these decisions. Throughout the course, we will examine how these empirical findings intersect with the ethical choices that we ought to make.






















